English Language Study Guide: Parts of Speech, Figurative Language, and Direct/Indirect Speech for FBISE Class 10
Parts of speech, Figurative language and
Direct and Indirect speech - Notes and exercises
FBISE Class 10
 Parts of speech
Parts of speech
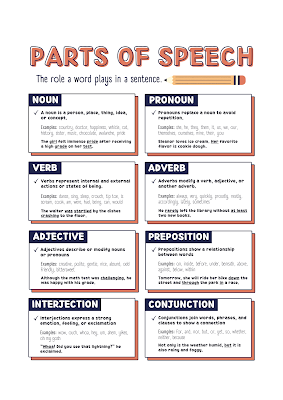
NOUN - (Naming word)
A noun is the name of a person, place, thing or idea.
Examples of nouns: Daniel, London, table, dog, teacher, pen, city,
happiness, hope
Example sentences: Steve lives
in Sydney. Mary uses pen and paper to write letters.
PRONOUN - (Replaces a Noun)
A pronoun is used in place of a noun or noun phrase to avoid
repetition.
Examples of pronouns: I, you, we, they, he, she, it, me, us, them, him,
her, this, those
Example sentences: Mary is tired. She wants to sleep. I want her to
dance with me.
ADJECTIVE - (Describing word)
An adjective describes, modifies or gives more information about a
noun or pronoun.
Examples: big, happy, green, young, fun, crazy, three
Example sentences: The little girl had a pink hat.
VERB - (Action Word)
A verb shows an action or state of being. A verb shows what
someone or something is doing.
Examples: go, speak, run, eat, play, live, walk, have, like, are, is
Example sentences: I like Woodward English. I study their charts
and play their games.
ADVERB - (Describes a verb)
An adverb describes/modifies a verb, an adjective or another adverb.
It tells how, where, when, how often or to what extent. Many adverbs
end in -LY
Examples: slowly, quietly, very, always, never, too, well, tomorrow,
here
Example sentences: I am usually busy. Yesterday, I ate my
lunch quickly.
PREPOSITION - (Shows relationship)
A preposition shows the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another
word. They can indicate time, place, or relationship.
Examples: at, on, in, from, with, near, between, about, under
Example sentences: I left my keys on the table for you.
CONJUNCTION - (Joining word)
A conjunction joins two words, ideas, phrases or clauses together in a
sentence and shows how they are connected.
Examples: and, or, but, because, so, yet, unless, since, if.
Example sentences: I was hot and exhausted but I still finished the
marathon.
INTERJECTION - (Expressive word)
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a strong feeling or
emotion. It is a short exclamation.
Examples: Ouch! Wow! Great! Help! Oh! Hey! Hi!
Example sentences: Wow! I passed my English test. Great! – Ouch!
That hurt.
Sometimes teachers include Articles as a ninth part of speech so we
have included it here. Note, an article is a type of adjective
ARTICLE - (Defining word)
An article is used before a noun. These are divided into definite (the)
and indefinite (a, an). Articles help define nouns.
Examples: a, an, the
Example sentences: I need a dictionary. The dictionary needs to be in
English.
Parts Of Speech Exercises- 1
Find out the correct and the most appropriate type of speech in the
following parts of speech exercises;
1. Sheela went to the stationary to purchase *books* ( __________
).
2. She went to the mall *but* ( __________ ) did not purchase
anything new.
3. I *liked* ( __________ ) *her* ( __________ ) better than
another classmate.
4. A beautiful girl was doing her tasks *quickly* ( __________ ).
5. *She*( __________ ) goes for the morning walk regularly.
6. When she was *lying*( )in the park an insect bit her.
7. *You* ( __________ ) took him by holding his hand.
8. A *rich* ( __________ ) man purchased a *stunning* (
__________ )jewellery.
9. *Hurrah! *( __________ ) I have cleared all examinations.
10. The kitten is hiding *under* ( __________ ) the table.
11. *Alas!* ( __________ ) He couldn’t come here.
12. The body of the cupboard is made of *iron*. ( __________
)
13. This is not *your* ( __________ ) pencil but his.
14. There is still some juice *in *( __________ ) the bottle.
15. Sheetal is *performing* ( __________ ) her
responsibilities properly.
16. The painting made by the artist is *almost*( __________ )
impeccable.
17. We shall not leave *unless* ( __________ ) you permit us.
18. The path is *to* ( __________ ) cross by.
19. The Jasmine flowers smell *sweet*. ( __________ )
20. She *frequently* ( __________ ) goes to the temple.
Here are some notes and exercises on parts of speech, figurative language, and direct and indirect speech for FBISE Class 10:
1. **Noun:** A word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. Example: dog, cat, table, love.
2. **Pronoun:** A word that replaces a noun in a sentence. Example: he, she, it, they.
3. **Verb:** A word that describes an action, occurrence, or state of being. Example: run, jump, laugh, is.
4. **Adjective:** A word that describes or modifies a noun. Example: big, happy, red, beautiful.
5. **Adverb:** A word that describes or modifies a verb, adjective, or other adverb. Example: quickly, slowly, very, too.
6. **Preposition:** A word that shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words in a sentence. Example: in, on, at, under.
7. **Conjunction:** A word that connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. Example: and, but, or, because.
8. **Interjection:** A word or phrase that expresses strong emotion or surprise. Example: Wow!, Ouch!, Hey!
**Figurative Language:**
1. **Simile:** A comparison between two unlike things using "like" or "as". Example: She is as brave as a lion.
2. **Metaphor:** A comparison between two unlike things without using "like" or "as". Example: Time is a thief.
3. **Personification:** Giving human qualities to non-human entities. Example: The wind whispered through the trees.
4. **Hyperbole:** Exaggerated statements or claims not meant to be taken literally. Example: I've told you a million times.
5. **Alliteration:** The repetition of consonant sounds at the beginning of words. Example: Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers.
6. **Onomatopoeia:** Words that imitate sounds. Example: Boom, buzz, hiss.
7. **Idiom:** A phrase or expression that has a figurative meaning different from its literal meaning. Example: It's raining cats and dogs.
8. **Irony:** A situation where the actual outcome is different from what was expected. Example: The fire station burned down.
**Direct and Indirect Speech:**
 **Direct Speech:**
**Direct Speech:**
In direct speech, the exact words of the speaker are quoted within inverted commas.
Example: She said, "I am going to the market."
**Indirect Speech:**
In indirect speech, the words of the speaker are reported without using quotation marks, and may be altered to fit into the sentence structure.
Example: She said that she was going to the market.
**Exercises:**
1. Identify the parts of speech in the following sentences:
- The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.
- She sings beautifully.
- The cat sat on the mat.
- John and Peter went to the park.
- Wow! That's amazing!
2. Identify the figurative language used in the following sentences:
- The stars danced playfully in the moonlit sky. (Personification)
- His words were a dagger in her heart. (Metaphor)
- The flowers whispered secrets to the wind. (Personification)
- She's as quiet as a mouse. (Simile)
- Time crept by like a wounded animal. (Simile)
3. Rewrite the following sentences from direct to indirect speech:
- Direct: "I will come to your party," said Sarah.
- Direct: "The train leaves at 3 o'clock," he said.
- Direct: "I love chocolate," she exclaimed.
- Direct: "Don't forget to water the plants," Mom said.
- Direct: "I have finished my homework," Tom announced.
These exercises should help reinforce the understanding of parts of speech, figurative language, and direct and indirect speech for Class 10 students.


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment